Measurement
of wire sizes - standard wire gauge - outside micrometer
Necessity of measurement of wire
size:
Ø The measurements determine the amount
of current that can safely pass through the wire without generating damages.
Ø Wire
gauge refers to the physical size and current carrying capacity of the wire.
Ø To
find out the thickness or diameter of a conductor we use SWG and outside Micro
meter.
Measurement of wire size by
Standard Wire Gauge:
The standard wire gauge measure the wire size in SWG
numbers from 0 to 36. According to the standards each number has an assigned
diameter in inch or mm. It should be noted that the higher the number of wire
gauge the smaller is the diameter of the wire. The slot in which the wire just
slides in is the correct slot and the SWG number could be read in the gauge
directly.
Measurement of wire size by
American Wire Gauge (AWG):
The American wire gauge is different from the
British standard wire gauge. In an American wire gauge (AWG) the diameter is
represented in mils rather than inch or mm. One mil is one thousandth part of an
inch.
Measurement
of wire size by Outside micrometers:
Outside Micrometers are
used for measuring the thickness or outside diameter of small
parts. They are industry standard measuring tools because of their high
accuracy/resolution and ease of use. It is used to measure a job, generally
within an accuracy of 0.01 mm.
The
parts of a micrometer
Frame:
The
frame is made of drop-forged steel or malleable cast iron.
Barrel/sleeve:
The
barrel or sleeve is fixed to the frame. The datum line and graduations are
marked on this.
Thimble:
The thimble is attached to the spindle and on the bevelled surface of the
thimble, the graduation is marked.
Spindle:
One end of the spindle is the measuring face. The other end is threaded and
passes through a nut. The threaded mechanism allows for the forward and
backward movement of the spindle.
Anvil:
The anvil is one of the measuring faces which is fitted on the micrometer
frame. It is made of alloy steel and finished to a perfectly flat surface.
Spindle
lock-nut: The spindle lock-nut is used to lock the spindle at
a desired position.
Ratchet
stop: The ratchet stop ensures a uniform pressure between
the measuring surfaces.
Specification:
Outside micrometers are available in ranges of 0 to 25 mm, 25 to 50 mm, and so
on. For electrician, to read the size of the wire 0 to 25 mm is suitable.
Least Count: Least count can be
defined as the smallest division on main scale to the total no of division on
circular scale.
Skinning of cables:
Skinning is the process of removing insulation from
the wire and cable. By using Electrician knife (at 200 angle to the
axis of the core or conductor) and wire stripper.
Wire Stripper:
A wire
stripper is a hand tool used by electricians, for removing the
protective coating of an electric wire in
order to replace or repair or joint the wire.
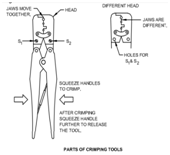
Crimping
tool:
Crimping tools are used
to make joints between two wires or a wire and a connector, such as lugs.
Cable Lugs:
Cable lugs are
used for connecting cables to
electrical appliances, other cables,
panel, surfaces, or mechanisms.
The current carrying capacity of a particular area
of cross section cable depends upon the following factors.
• Type of conductors
(metal)
• Type of insulation
• Cable run in conduit
or in open surface
• Single or three phase
circuit
• Type of protection -
coarse or close excess current protection
• Ambient temperature
• Number of cables in
bunches
• Length of circuit
(permissible voltage drop) - this will be discussed at a later stage.
Depending upon the above factors the current rating
of cables may vary to a great extent. Information in this lesson will enable
the wireman to select the correct cable under normal working conditions
Classification
of voltage grading:
Voltage is classified as
1. Low voltage (L.V):
Normally not exceeding 250V (i.e.) from 0 to 250 volts.
2. Medium voltage
(M.V): Exceeding 250V but not exceeding 650V from 250 to 650 volts
3. High voltage (H.V):
Exceeding 650V but not exceeding 33000V.(650-33000 volts)
4. Extra high voltages:
All voltages above 33000V comes under this category.





















0 Comments